🧬 Leukaemia Quiz: Pathophysiology and Clinical Patterns
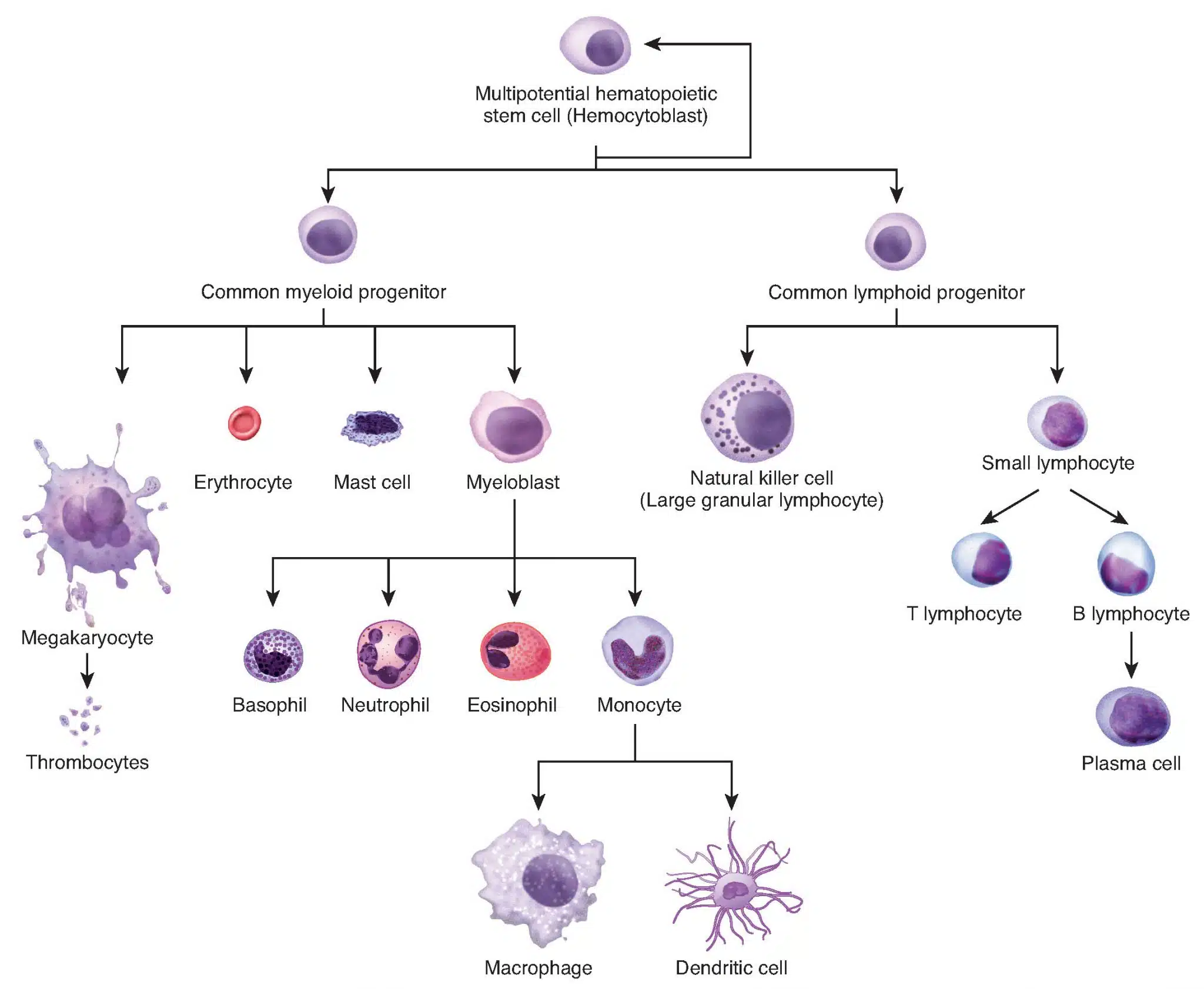
Test your understanding of leukaemia subtypes, diagnostic markers, and disease progression. This quiz features five case-based questions focused on acute and chronic leukaemias, suitable for second-year medical students learning about haematological malignancy.
No comments:
Post a Comment