👋 Let’s dive into the fascinating (and complex) world of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)—a classic autoimmune disorder that’s important to understand for future clinical practice. 🩺📚
Monday, 10 November 2025
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Unravelling the Pathophysiology 🧬
Thursday, 6 November 2025
Antiphospholipid syndrome: A prothrombotic puzzle
Pathophysiology of antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder characterised by the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL), which target phospholipid-binding proteins involved in coagulation. These antibodies disrupt normal endothelial function, leading to hypercoagulability and an increased risk of thrombosis.
Wednesday, 5 November 2025
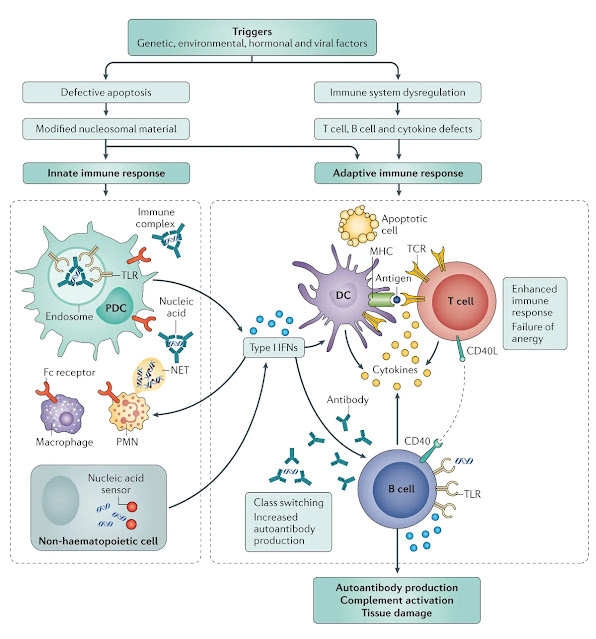
Understanding the pathophysiology of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterised by multisystem involvement and a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. It primarily affects young women and can manifest with diverse clinical symptoms, ranging from mild cutaneous involvement to life-threatening organ damage. Understanding its pathophysiology is crucial for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Tuesday, 4 November 2025
Immune Tolerance & The Development of Autoimmunity
The immune system functions as a highly selective defence network, recognising foreign pathogens while preserving self-tolerance to avoid attacking the body’s own tissues. This balance is essential for immune homeostasis—but when tolerance mechanisms break down, autoimmune diseases develop, causing chronic inflammation and tissue destruction.
Understanding how immune tolerance is established, maintained, and eventually fails provides critical insight into the pathophysiology of autoimmunity.