-
A 52-year-old woman presents with oedema and frothy urine. Urinalysis reveals heavy proteinuria, but no haematuria. Her serum albumin is low.
Which of the following best describes the role of the glomerulus in the nephron?
Explanation: The glomerulus filters blood plasma into Bowman’s capsule. This is the first step in urine formation, where water and small solutes are filtered from the blood into the nephron.
-
A 35-year-old man is recovering from acute dehydration. Blood tests reveal a mild elevation in creatinine, but urine sodium is low and urine osmolality is high.
Which part of the nephron is most responsible for bulk reabsorption of filtered sodium and water?
Explanation: The PCT reabsorbs around 65% of filtered sodium and water, as well as nearly all glucose, amino acids, and bicarbonate. This is crucial for maintaining homeostasis.
-
A 24-year-old man is lost in the desert for two days with minimal water intake. His kidneys activate mechanisms to conserve water while still clearing solutes.
In the Loop of Henle, the descending limb is permeable to _____, while the ascending limb actively transports _____ out of the filtrate.
Explanation: The descending limb is permeable to water, while the ascending limb actively transports sodium, potassium, and chloride. This creates a gradient used for urine concentration.
-
A 68-year-old woman with congestive heart failure is prescribed spironolactone. On review, her potassium level is elevated.
Which hormone is most responsible for increasing sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion in the distal nephron?
Explanation: Aldosterone acts on the distal tubule and collecting duct to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion. It is part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
-
A 76-year-old man with long-standing heart failure is admitted with hyponatraemia and low serum osmolality. His urine remains concentrated despite low sodium.
Which of the following best explains how his kidneys can still concentrate urine?
Explanation: Countercurrent multiplication in the Loop of Henle establishes a hyperosmotic medullary interstitium, allowing water reabsorption in the collecting duct and concentration of urine.
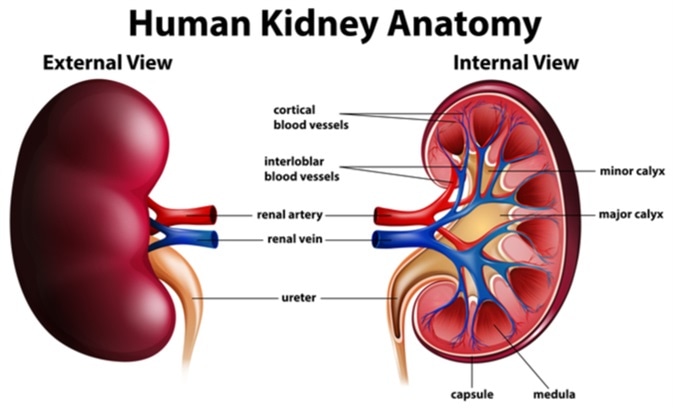 Test your understanding of nephron structure and kidney physiology with these five quiz questions.
Want to try more quizzes?
Test your understanding of nephron structure and kidney physiology with these five quiz questions.
Want to try more quizzes?
No comments:
Post a Comment